Credit
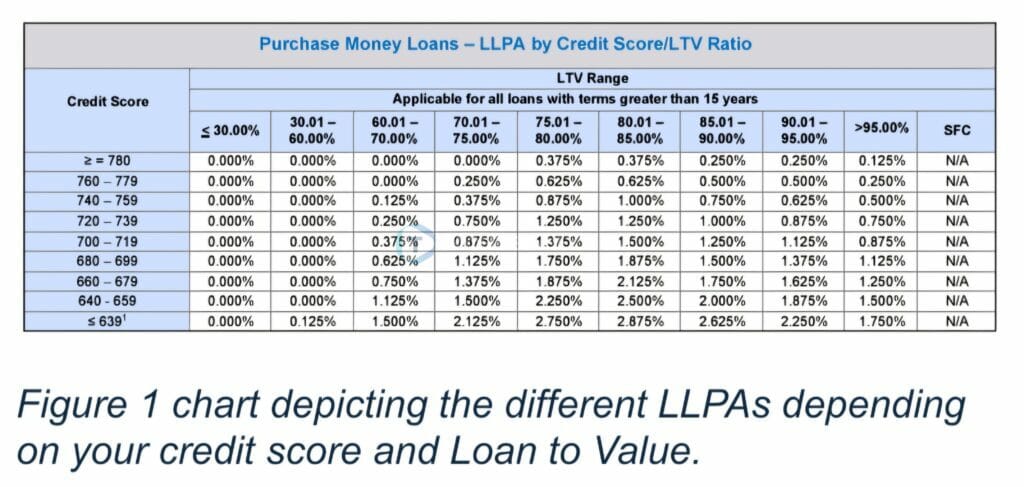
Your credit score is one of the most critical factors influencing your mortgage rate. Maintaining a strong credit score ensures you receive the best possible interest rate. Lenders apply Loan Level Price Adjustments (LLPA) for scores below 780, using 20-point tiers (e.g., 779–760, 759–740).
Actions to Improve Your Credit Score
- Credit Utilization: Keep your credit utilization below 9% for an optimal score. Requesting a credit limit increase can help but may result in a hard credit inquiry.
- Credit History: Keep your oldest credit cards active and in regular use to lengthen your credit history.
- Authorized User: Being added as an authorized user to a well-established account with a strong payment history can quickly boost your score.
- Check Your Credit Report: Regularly monitor your credit report for errors or changes. Use free reports from credit bureaus or services like Credit Karma for alerts.
Down Payment
Your loan-to-value ratio (LTV) also affects your mortgage rate. While larger down payments typically lower rates, some government programs offer better rates to borrowers with smaller down payments to assist specific demographics. However, if your down payment is less than 20%, expect to pay Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI).
Mortgage Types and Terms
Work with your mortgage broker to explore different programs, such as 30-year or 15-year terms, and fixed or adjustable-rate mortgages. Each option offers unique benefits depending on your financial goals.
In Conclusion
Improving your mortgage rate begins with reviewing your credit report and taking steps to boost your credit score. For instance, a borrower I recently advised increased their credit limit by contacting their credit card company, raising their credit score by nearly 40 points. Small, strategic actions can significantly impact your ability to secure a favorable rate.